Why Anti Money Laundering Matters in 2025 and Beyond
Couple of years back, international investigators uncovered how a global crime syndicate laundered over $4 billion through shell companies, crypto wallets, and trade-based schemes. The money fuelled everything from narcotics networks to terror financing operations.
What made the case even more alarming wasn’t just the size, it was how seamlessly illicit funds blended into the legitimate economy, escaping traditional oversight until it was almost too late.
This is why anti-money laundering (AML) measures matter more than ever. In today’s world, money laundering isn’t just a financial crime; it’s a national security threat, a systemic risk to global economies, and a stain on institutional trust.
Every dollar successfully laundered strengthens criminal networks, destabilizes financial institutions, and weakens the fight against organized crime and terrorism.
By 2025, with the explosive growth of digital banking, cross-border payments, and cryptocurrencies, AML has evolved far beyond a regulatory checkbox.
It is now a strategic shield for protecting economies and societies. The question is no longer just “Are we compliant?” – but “Are we resilient against financial crime?”
This blog explores AML from the ground up: its foundations, pillars, methods, challenges, and how AI-driven transaction monitoring and intelligence-led approaches are reshaping the fight.
What is Anti-Money Laundering (AML)?
At its core, Anti-Money Laundering (AML) refers to the laws, processes, and technologies designed to prevent criminals from disguising illicit funds as legitimate earnings.
The goal is simple yet critical: stop dirty money from entering the financial system, where it could otherwise be used to finance crime, corruption, or terrorism.
While Anti Money Laundering is often associated with banks, its scope extends far wider today. Fintech platforms, cryptocurrency exchanges, casinos, real estate, and even cross-border trade networks are all under scrutiny, because each presents potential loopholes for laundering illicit funds.
AML vs Counter-Terrorism Financing (CTF)
Though closely related, AML and CTF are not the same:
- Anti Money Laundering focuses on preventing criminals from hiding the origins of illegally obtained money.
- Counter-terrorism Financing targets the flow of funds used to support terrorist activities, which may not always originate from illegal sources (e.g., charitable donations diverted to extremist networks).
Together, AML and CTF form the global financial crime prevention framework that regulators, banks, and governments rely on to secure financial ecosystems.
In today’s digital-first economy, AML is not just compliance – it’s defence. Whether it’s a suspicious crypto transaction, a fraudulent cross-border transfer, or a shell company buying luxury real estate, AML systems provide the first line of protection.
The Stages of Money Laundering
Money laundering is rarely a single act. Instead, it unfolds in three stages – Placement, Layering, and Integration, each designed to distance illicit funds from their criminal origins.
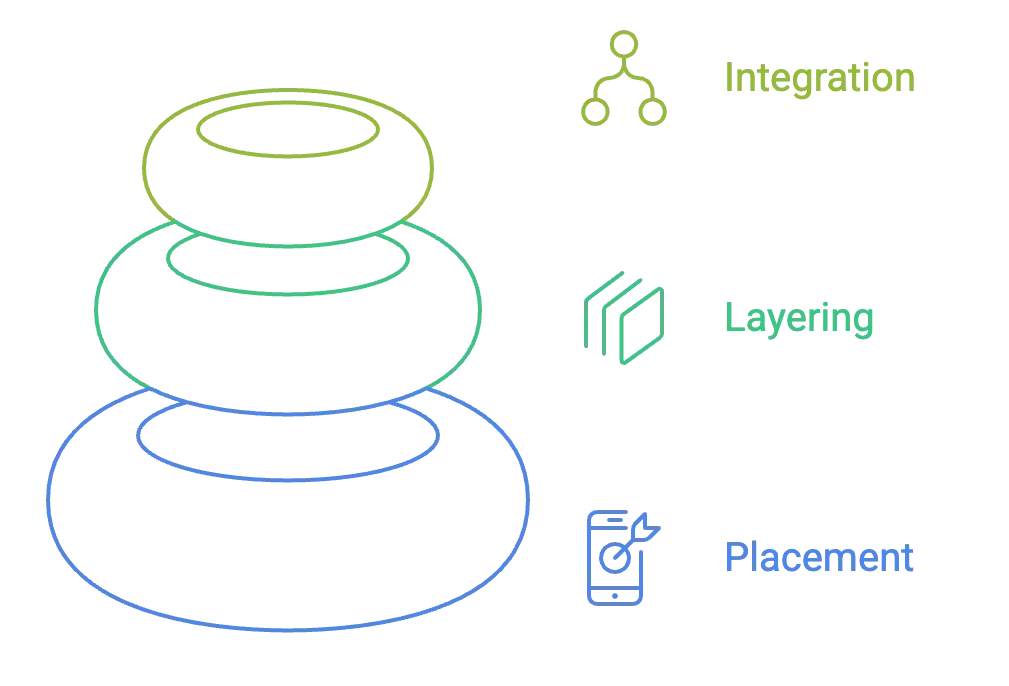
Placement
This is where “dirty money” first enters the financial system. Criminals might deposit cash into banks, buy high-value goods like luxury cars or jewellery, or use casinos and online platforms to disguise cash inflows.
👉 Example: A drug trafficker deposits small amounts of cash into multiple accounts to avoid raising suspicion (a tactic known as “smurfing”).
Layering
Once inside the system, the money is moved through complex transactions to obscure its trail. This could involve:
- Transferring funds across multiple accounts and jurisdictions.
- Using shell companies to mask ownership.
- Converting money into cryptocurrencies or other assets.
👉 Example: The trafficker wires funds through offshore accounts, invests in shell corporations, and converts a portion into Bitcoin.
Integration
Finally, the funds re-enter the legitimate economy, appearing “clean”. Criminals might:
- Invest in real estate.
- Start seemingly legitimate businesses.
- Use the money for luxury investments (art, yachts, etc.).
👉 Example: The trafficker uses laundered money to buy real estate under a company name, making it nearly impossible to link back to crime.
Why These Stages Make Detection Difficult
Each stage is designed to break the chain of evidence. By the time illicit money reaches the integration phase, it’s almost indistinguishable from legitimate funds.
This complexity is why modern Anti-money Laundering systems rely on advanced analytics, link analysis, and AI-driven transaction monitoring to detect suspicious activity across borders and industries.
The 5 Pillars of Anti Money Laundering Compliance
To understand how institutions protect themselves from financial crime, picture yourself as a bank officer welcoming a new client. Behind every interaction lies a framework designed to prevent money laundering and safeguard the financial system.

This framework is built on the five pillars of AML compliance.
1. Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
Before opening an account, you verify who the customer really is. This involves:
- Collecting official documents (KYC checks).
- Assessing risk profiles (low-risk salaried professional vs. high-risk offshore entity).
- Ongoing monitoring of transactions for unusual activity.
👉 Without CDD, you’d be opening the door to anonymous money laundering.
2. Internal Policies & Controls
As a compliance officer, you rely on internal rules, monitoring tools, and escalation procedures that guide how suspicious transactions are flagged and investigated.
👉 Think of this as the immune system of your institution, constantly scanning for threats.
3. Appointment of a Compliance Officer
Every institution needs a designated AML compliance officer. This person ensures policies are followed, regulatory reports are filed, and the institution remains audit-ready.
👉 Imagine this officer as the captain of the compliance ship, steering it safely through regulatory waters.
4. Training & Awareness
Employees at all levels, from tellers to senior managers, must recognize red flags like structuring deposits, unusual cross-border transfers, or politically exposed persons (PEPs).
👉 Without training, even the most advanced monitoring system becomes ineffective, because human judgment is the first line of defence.
5. Independent Audit
Finally, an independent audit ensures the AML framework is not just on paper but working in practice. Auditors test policies, review cases, and suggest improvements.
👉 It’s the equivalent of a health check-up for your compliance system.
Why the 5 Pillars Matter
Together, these five pillars form a living framework that keeps financial institutions resilient. They’re not static rules but evolving practices, especially as criminals invent new laundering methods using fintech, crypto, and global trade.
Different Types of Anti Money Laundering Programs
Not all anti-money laundering efforts are the same. Financial institutions implement different types of AML programs, each playing a unique role in safeguarding against financial crime.
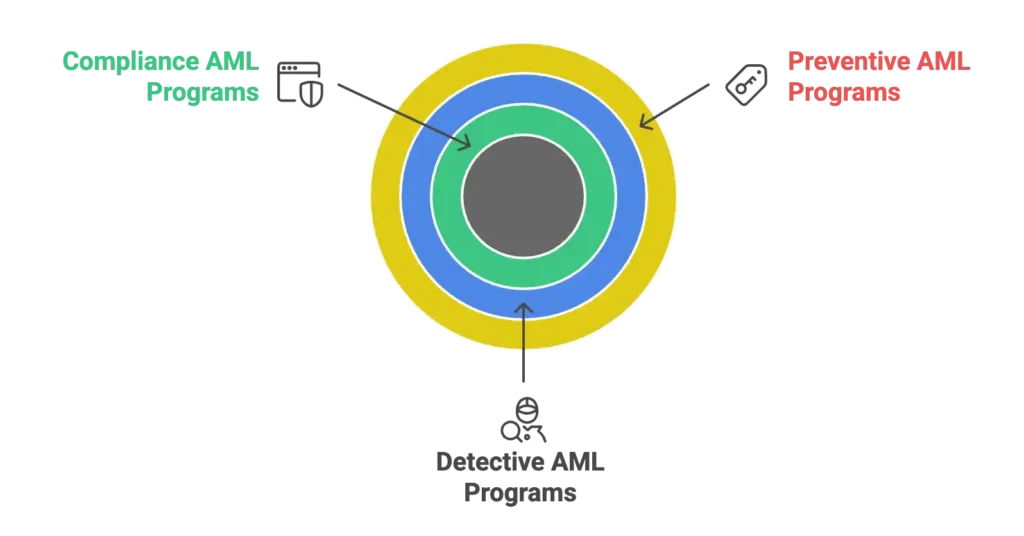
Think of it like airport security, multiple layers working together to ensure safety:
Preventive Anti-Money Laundering Programs
These are the first line of defence against money laundering. They include:
- Know Your Customer (KYC): Verifying customer identity at onboarding.
- Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD): Extra checks for high-risk clients such as offshore companies or politically exposed persons (PEPs).
- Risk-based onboarding: Assessing and assigning risk profiles before account approval.
👉 Just like checking IDs before entering an airport, preventive AML stops suspicious actors at the gate.
Detective Anti-money Laundering Programs
Even with prevention, criminals often slip through. That’s where detective AML comes in, focusing on spotting red flags in real time, such as:
- AML transaction monitoring: Scanning customer activity for unusual transfers, structuring, or layering.
- Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs): Filing reports when patterns suggest illicit behavior.
- Link analysis & network mapping: Detecting hidden connections between entities.
👉 Similar to the X-ray scanner at airport security, these tools look deeper to uncover hidden risks.
Compliance AML Programs
Compliance programs ensure that institutions align with regulatory frameworks and demonstrate accountability. These include:
- Internal AML policies & procedures
- Compliance officer oversight
- Independent audits & regulatory reporting
👉 Think of this as following aviation safety laws, not just keeping people safe, but proving to regulators that every protocol is in place.
Why Multiple Anti Money Laundering Programs Matter
When combined, these programs create a layered defence system. Preventive controls stop risks at the door, detective systems catch suspicious activities in flight, and compliance programs ensure the entire institution remains both safe and legally sound.
AML Checks – How Institutions Detect Suspicious Activity
When it comes to fighting financial crime, AML checks are the frontline safeguards. They ensure that every customer and transaction passing through a financial institution is vetted against known risk factors.
These checks combine regulatory compliance with advanced technology to prevent suspicious actors from slipping through the cracks.
Let’s break down the core AML screening processes:
KYC Verification & Customer Profiling
Every AML program begins with Know Your Customer (KYC). Banks and fintechs verify customer identity using official documents, biometrics, and background information. Beyond identity, institutions build customer profiles that include:
- Expected transaction types
- Geographic exposure
- Occupation and risk rating
👉 This ensures that when unusual activity occurs, it can be flagged against the baseline profile.
Sanctions Screening
Financial institutions are required to check all clients and counterparties against international sanctions lists such as:
- UN Sanctions List
- OFAC (Office of Foreign Assets Control)
- EU Consolidated List
A single match can freeze accounts or block a transaction, preventing funds from reaching terrorists, proliferators, or rogue states.
Ongoing Monitoring
AML checks are not one-time events. Continuous monitoring of transactions, geolocation patterns, and sudden spikes in activity helps institutions catch money laundering attempts in real time. AI-driven monitoring tools are increasingly used to adapt detection to evolving typologies.
Case Study: How One Flagged Transaction Prevented Global Laundering
In 2020, a European bank flagged a $250,000 wire transfer to an obscure offshore entity during routine sanctions screening. Upon deeper investigation, the entity was linked to a wider network of shell companies tied to a sanctioned regime.
- Without this one flagged transaction, millions could have flowed into global black markets undetected.
- The case highlighted how AML checks act not just as regulatory compliance, but as critical tools in safeguarding global security.
Why AML Checks Matter
Each layer, from KYC to sanctions and PEP checks, works like a net, catching risks at different stages. Together, they make financial systems harder to exploit and ensure that institutions aren’t unintentionally complicit in global money laundering.
AML Transaction Monitoring – The Heart of Detection
If AML compliance were a fortress, transaction monitoring would be the watchtower. It is the core function that allows institutions to detect suspicious activity in real time, ensuring that laundered money doesn’t slip unnoticed into legitimate financial systems.
Why AML Transaction Monitoring Matters
Every day, billions of transactions flow across banks, fintechs, and payment networks. Hidden within these are attempts to:
- Layer illicit funds through multiple accounts
- Use “smurfing” techniques (breaking large sums into small deposits)
- Disguise money through trade finance or cross-border transfers
AML transaction monitoring gives institutions the eyes to catch these anomalies, often within seconds.
How AML transaction monitoring Works
Rule-Based Alerts
Traditional monitoring systems use pre-set rules like:
- “Flag transfers above $10,000”
- “Alert if more than 5 deposits occur within an hour”
This provides a baseline, but alone, it often leads to too many false positives.
Behavioural Analytics
Instead of just looking at numbers, advanced systems study customer behaviour over time.
👉 For example, a business account suddenly sending funds to a high-risk jurisdiction would trigger alerts even if the amount was small.
Machine Learning & AI Models
Modern AML monitoring leverages AI-driven data analytics to adapt to new laundering patterns. Unlike static rules, these models learn from past cases, evolving as criminals change tactics.
The Challenge – High False Positives
One of the biggest hurdles in AML transaction monitoring is noise:
- Up to 95% of alerts in traditional systems turn out to be false positives.
- This overwhelms compliance teams, leading to delays or missed genuine cases.
That’s why next-generation AML monitoring software focuses on precision, reducing false positives while catching complex laundering schemes.
The Innefu Advantage – Prophecy Eagle I
While many monitoring tools stop at alerts, Prophecy Eagle I goes deeper:
- Entity Resolution: Unmasks hidden relationships between accounts, companies, and individuals.
- Link Analysis: Maps entire laundering networks, not just single suspicious transactions.
- AI-Driven AML Monitoring: Continuously adapts to evolving money laundering typologies, improving accuracy and reducing compliance fatigue.
- Vendor Client Due Diligence: Scans the Surface and Deep Web to provide real-time threat scores for proactive risk evaluation.
- Threat Scoring of GST/Account: Multi-layered risk assessment using facial biometrics, device fingerprints, IP analysis, and OSINT monitoring.
- Synthetic ID Detection: Access a comprehensive facial library of financial absconders, tax evaders, and accused individuals to detect duplicate IDs for bank accounts and prevent identity fraud.
- GIS Analysis: Ingest location information from various sources and geo-tagged files to perform location-based analysis and track geographic patterns in financial transactions.
This transforms monitoring from a box-ticking exercise into a true intelligence function, giving financial institutions foresight, not just hindsight.
Learn more about Prophecy Eagle I.
Cybercrime, Crypto, and the New AML Frontiers
Money laundering today doesn’t always flow through banks or cash deposits. Increasingly, it hides in the digital shadows of cybercrime, cryptocurrencies, and dark web markets, making the job of compliance teams more complex than ever.
The Cybercrime Connection
Organized crime groups and even state-sponsored actors rely on laundering to move proceeds from:
- Ransomware attacks (where victims pay in cryptocurrency).
- Phishing and identity theft (stolen funds laundered through online payment platforms).
- Dark web marketplaces (illegal goods traded with digital assets).
The speed and anonymity of the internet make these schemes harder to trace compared to traditional banking methods.
Cryptocurrency – The Double-Edged Sword
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Monero present both challenges and opportunities:
- Challenge: Criminals use “mixers” and “privacy coins” to obscure ownership trails. A single laundering cycle can involve hundreds of wallets, making detection a needle-in-a-haystack problem.
- Opportunity: Blockchain itself is transparent. With the right AML and crypto monitoring tools, investigators can analyze transaction histories and uncover patterns.
This has led to a rise in specialized RegTech (Regulatory Technology) solutions, which bring AI and blockchain analytics into AML programs.
The Rise of RegTech and AI in Anti Money Laundering
To keep up with these new frontiers, financial institutions are turning to:
- AI-Driven Analytics: Machine learning models that detect unusual wallet activities and trace crypto transactions across multiple exchanges.
- Automated KYC & Screening: Real-time customer verification for digital-first banks and fintech platforms.
- Cross-Domain Integration: Combining cyber forensics, OSINT, and financial monitoring to create a unified picture of illicit activity.
This is where Anti Money Laundering compliance intersects with cybersecurity and AI, enabling institutions to stay one step ahead of increasingly sophisticated launderers.
Anti Money Laundering and National Security

When most people hear Anti-Money Laundering (AML), they think of banks ticking regulatory checkboxes. But in reality, AML is far more than financial compliance, it is a national security imperative.
The Security Dimension of AML
Terror networks and organized crime groups often move money not in millions, but in small, frequent, and seemingly harmless transactions. For example:
- A terror cell may fund logistics by routing small payments through charities.
- A trafficking network might cycle microtransactions through online wallets.
- State-sponsored groups could mask cyberattack proceeds using crypto mixers.
On their own, these payments may appear benign. But when stitched together through AML monitoring and intelligence fusion, they reveal the financial scaffolding of entire illicit networks.
Case Study – The Hidden Financing Trail
In one well-documented case, counterterrorism agencies uncovered how funds were moved in increments of just a few hundred dollars across borders to finance a large-scale operation.
Traditional monitoring systems flagged nothing, but integrated AML and intelligence fusion analysis exposed the pattern in time.
This is why modern AML is not just about banking oversight – it’s about threat prevention.
The Intelligence Fusion Advantage
To make AML truly mission-ready, financial monitoring must converge with broader intelligence streams:
- OSINT & Social Media Surveillance → linking suspicious fund flows to groups flagged online.
- CDR & Communication Mapping → connecting fund transfers to human networks.
- Defence & Homeland Security Databases → fusing financial anomalies with cross-border security alerts.
This is where Intelligence Fusion Centres (IFCs) step in, serving as nerve hubs that combine financial data, cyber intel, and national defence insights.
Innefu’s Perspective

At Innefu, we view AML not as a compliance checkbox, but as a pillar of national security resilience. Our Prophecy Eagle I platform goes beyond transaction monitoring by enabling:
- Entity Resolution & Link Analysis → connecting fragmented financial trails.
- AI-Powered AML Monitoring → reducing false positives and surfacing hidden typologies.
- Fusion Capabilities → integrating AML with defence, law enforcement, and cyber intelligence systems. And more.
This ensures that AML is not siloed inside banks but woven into the fabric of national security strategy.
Future of Anti-Money Laundering: AI, Machine Learning, and Predictive Analytics
The next decade will redefine how we fight money laundering. As financial systems become faster, digital-first, and increasingly global, traditional rule-based AML approaches will no longer be enough. The future lies in AI-driven, predictive systems that move from reactive compliance to proactive intelligence.
Predictive Anti Money Laundering Systems
Instead of waiting for suspicious transactions to occur, predictive analytics uses historical laundering typologies, behavioural patterns, and real-time signals to anticipate risk. For instance:
- Spotting layered transfers designed to mask origins before they complete.
- Forecasting high-risk customers by analysing transaction velocity, geographies, and entity links.
This allows institutions to intervene before funds disappear into the shadows.
Entity Resolution and Link Analysis
Criminal networks rarely operate in isolation. They build webs of accounts, shell companies, and intermediaries to stay hidden. Advanced entity resolution technologies merge fragmented identities across multiple banks, jurisdictions, and transaction records.
When combined with AI-powered link analysis, these tools reveal hidden relationships, such as the same entity controlling five different companies across three countries.
This shift transforms AML from box-ticking into network disruption.
Generative AI for Investigators
Generative AI and LLM-powered systems (in air-gapped, on-premise environments) can ease the investigative burden by:
- Auto-generating case summaries from thousands of transactions.
- Drafting suspicious activity reports (SARs) with supporting evidence.
- Creating risk dashboards that highlight priority alerts.
This doesn’t replace investigators, it augments them, freeing analysts from repetitive work and helping them focus on high-value decision-making.
From Compliance to Intelligence
The most profound transformation is cultural: AML will no longer be seen as just compliance. Instead, it becomes a core intelligence function, closely tied to counterterrorism, cybersecurity, and national security objectives.
Conclusion – Anti Money Laundering as the First Line of Financial Defence
Money laundering is more than an economic crime – it’s a threat multiplier that fuels terrorism, organized crime, and corruption worldwide. As financial systems grow faster and more complex, the stakes for detection and prevention have never been higher.
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) today is not just about compliance with regulators. It’s about safeguarding national security, protecting institutions, and building trust in global markets.
From the five pillars of compliance to AI-driven transaction monitoring and predictive analytics, AML is evolving into an intelligence-led discipline. Institutions that embrace this shift will not only stay compliant but also gain the resilience to anticipate threats rather than just react to them.
The future of AML isn’t just regulatory – it’s strategic, and it’s already here.
FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions
Why is AML important for financial institutions?
AML is important because it protects financial institutions from being used by criminals, reduces regulatory risks, prevents reputational damage, and strengthens trust with customers and regulators.
What is the difference between AML and CTF?
AML focuses on preventing money laundering, while Counter-Terrorism Financing (CTF) targets the detection and prevention of funds that are used to support terrorist activities.
How does AI help in AML?
AI helps in AML by detecting hidden patterns in large volumes of financial data, reducing false positives, performing link analysis across entities, and even using predictive analytics to spot suspicious behaviour before it occurs.
Who regulates anti-money laundering globally?
Globally, the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) sets AML standards. Countries then implement their own AML laws through central banks, financial intelligence units (FIUs), and regulators.
How does AML impact cryptocurrency exchanges?
Crypto exchanges must follow AML regulations such as KYC verification, transaction monitoring, and suspicious activity reporting to prevent laundering through digital assets.
What industries are most vulnerable to money laundering?
Apart from banking, high-risk sectors include fintech, real estate, casinos, insurance, and cross-border trade, all of which can be exploited for laundering.
What is the difference between AML and KYC?
KYC (Know Your Customer) is one component of AML, focusing on verifying a customer’s identity at onboarding. AML is broader, covering ongoing monitoring, transaction screening, and suspicious activity detection.
Can AI completely replace human compliance officers in AML?
No. AI improves speed, accuracy, and predictive detection, but human judgment is critical for contextual analysis, decision-making, and regulatory compliance.
How do Anti Money Laundering systems reduce false positives?
Modern AML tools use behavioural analytics, machine learning, and entity resolution to distinguish between unusual but legitimate activity and true suspicious behaviour, lowering false alerts.
Why is AML critical for national security?
Because money laundering often finances terrorism, organized crime, and corruption. AML helps disrupt these networks, making it a cornerstone of both financial integrity and security strategy.
What are future trends in AML technology?
Trends include real-time monitoring, AI-driven link analysis, predictive analytics, and generative AI for risk summaries and reports. These are transforming AML from compliance to intelligence.




