Introduction: Why Crime Pattern Analysis Matters
In 2017, a mid-sized European city faced a wave of burglaries. Despite increased patrols, the crimes persisted until police analysts dug into historical burglary data.
They noticed a repeating pattern: the same days of the week, the same entry points, and similar neighbourhoods. With this knowledge, they redeployed patrols strategically – burglaries dropped by 30% within months.
Instead of reacting after crimes occur, agencies can predict, prevent, and disrupt by learning from history.
Also read: Crime Prediction Using Machine Learning
What is Crime Pattern Analysis?

Crime pattern analysis is the process of systematically examining past crime data to uncover recurring behaviours, trends, and relationships that criminals exploit.
- It’s not just about storing crime data – it’s about contextual intelligence.
- Analysts look at who committed the crime, where it happened, when it occurred, and how it was executed.
- These insights enable law enforcement to make data-backed decisions, from resource allocation to suspect identification.
📌 Examples across domains:
- Law enforcement: Identifying burglary sprees tied to repeat offenders.
- Financial crime: Detecting fraudsters who recycle the same laundering methods every few years.
- Counter-terrorism: Recognizing similarities in bomb-making tactics across different groups.
Key Data Sources in Crime Pattern Analysis
Patterns only emerge when fragmented intelligence streams are fused together.
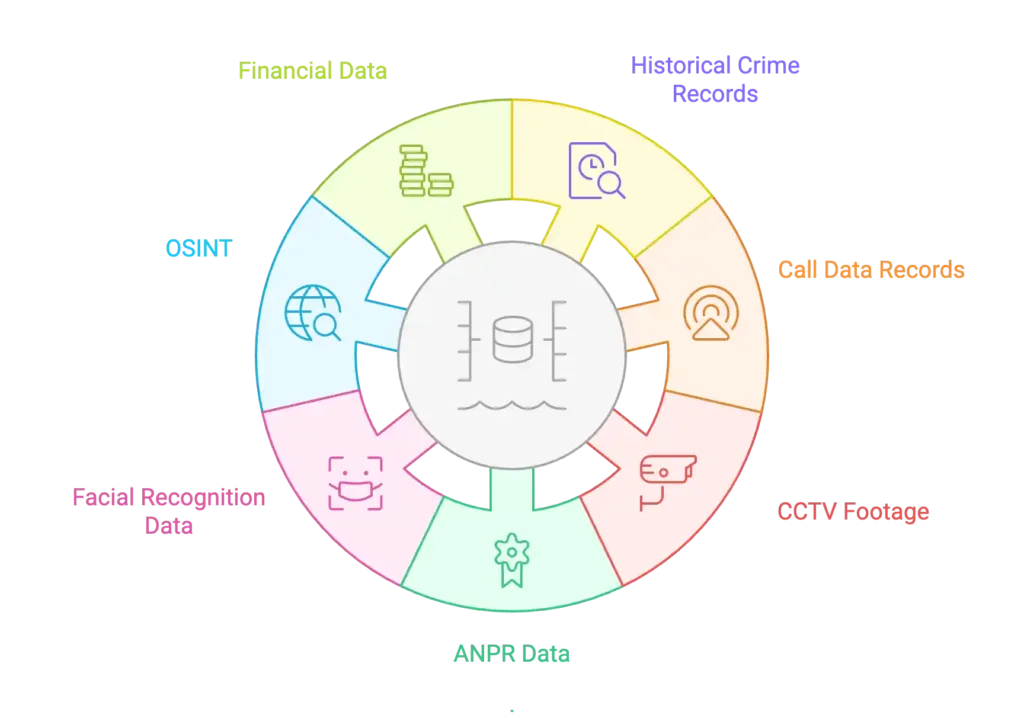
Common data sources include:
- Historical crime records – police case files, FIRs, charge sheets.
- Call Data Records (CDRs) – mapping associations, identifying networks.
- CCTV footage & surveillance – powered by AI Vision, detecting anomalies in movement or behaviour.
- Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR) – tracking vehicle movements across hotspots.
- Facial recognition data – matching known offenders across locations.
- Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT) – social media chatter, news, dark web forums, analysed with Innsight.
- Financial data – AML monitoring, suspicious activity reports, useful for white-collar crime.
💡 The richer the dataset, the stronger the patterns, but this requires powerful fusion platforms to avoid data silos.
Analytical Techniques Used
Crime pattern analysis depends on combining statistical, geospatial, and AI-driven methods.
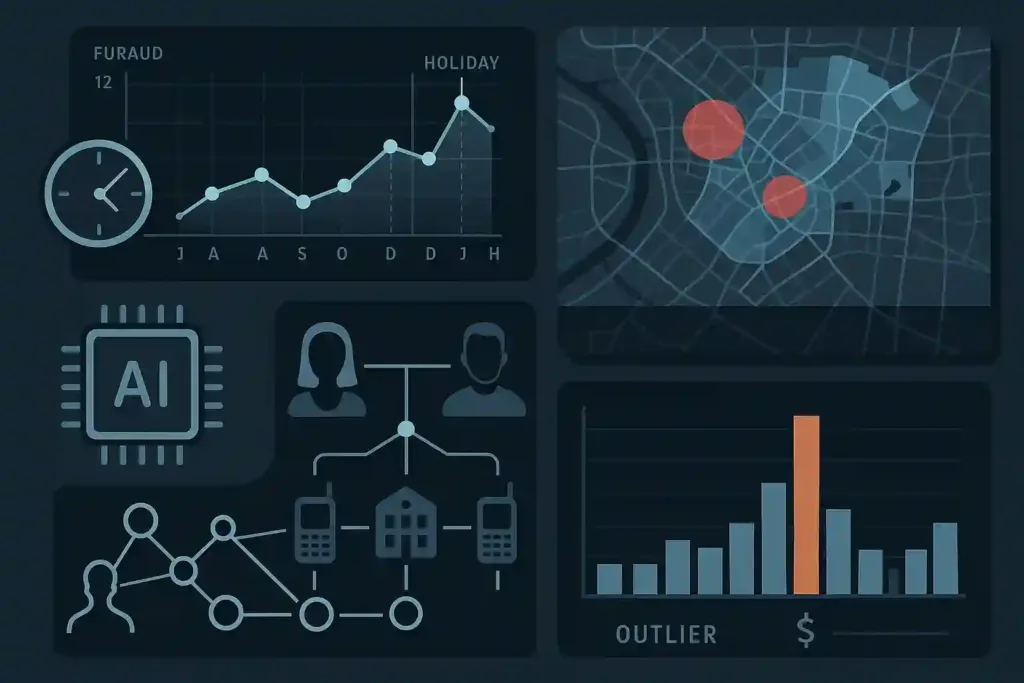
Key techniques:
- Temporal Analysis: Studying time-series data to find seasonal or time-of-day trends.
👉 Example: A surge of ATM fraud during holiday weekends.
- Spatial Analysis (GIS Mapping): Visualizing hotspots geographically.
👉 Example: Mapping vehicle thefts to identify city “hot zones.”
- Link Analysis: Uncovering relationships between suspects, devices, and entities.
👉 Example: Using Intelelinx to connect a fraud network operating via burner phones.
- Behavioral Profiling: Detecting modus operandi similarities across cases.
👉 Example: Burglars consistently entering via rooftops in high-density areas.
- Anomaly Detection with AI: Highlighting outliers in datasets, such as sudden spikes in small-value wire transfers.
These techniques together convert raw datasets into crime intelligence.
From Historical Data to Prediction
The true strength of crime pattern analysis lies in moving from hindsight to foresight.
- Historical burglary data → identifies emerging neighbourhood hotspots.
- Repeated fraud typologies → flags recycled laundering techniques.
- Smuggling networks → detect old infiltration routes reappearing years later.
Modern platforms fuse historical + live data, enabling real-time alerts. For example, Prophecy Alethia combines CDR, ANPR, OSINT, and facial recognition to forecast risks dynamically.
Benefits of Crime Pattern Analysis
Agencies worldwide are investing in crime pattern analysis because it delivers tangible operational benefits:

- Proactive deployment: Smarter patrol allocation and targeted checkpoints.
- Faster investigations: Analysts instantly surface related cases, suspects, and evidence.
- Institutional memory: Prevents knowledge loss when analysts retire or transfer.
- Community safety: Deters crime by disrupting repeat behaviours.
- Cross-agency collaboration: Enables intelligence fusion across police, defence, and financial regulators.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its potential, it faces real-world hurdles:
- Data silos: Different agencies (police, defence, FIUs) often hoard their intelligence.
- Unstructured data: Text reports, video feeds, and CDR logs are difficult to analyse without AI.
- Bias risks: Predictive systems may reinforce historical biases unless carefully monitored.
- Over-reliance on automation: Algorithms should support, not replace, human judgment.
- Resource constraints: Smaller agencies may lack infrastructure for big data analytics.
💡 The solution lies in AI-driven fusion centres, where platforms like Prophecy Guardian and Alethia unify intelligence without compromising oversight.
Innefu’s Role in Crime Pattern Analysis
At Innefu, we enable agencies to turn history into foresight. Our suite of solutions creates a single intelligence backbone:
- Prophecy Alethia → predictive policing, crime hotspot mapping, and case building.
- Innsight → OSINT platform that detects disinformation campaigns, extremist chatter, or fraud signals.
- Intelelinx → advanced CDR analysis software for dismantling organized crime networks.
- AI Vision → AI-powered video analytics for anomaly detection and forensic replay.
Conclusion: From Patterns to Prevention
Crime pattern analysis bridges yesterday’s intelligence with tomorrow’s security. By detecting recurring behaviours, fusing siloed datasets, and applying AI-driven analytics, agencies can disrupt crime before it escalates.
👉 Request a demo to see how Innefu transforms crime patterns into actionable foresight.
FAQ Section
Q1. What is crime pattern analysis in law enforcement?
It’s the study of recurring trends in criminal activity to forecast future risks and improve policing strategies.
Q2. How does crime pattern analysis differ from crime prediction?
Analysis focuses on understanding past behaviours, while prediction uses those insights to forecast future crimes.
Q3. What are the main techniques used in crime pattern analysis?
Temporal, spatial (GIS mapping), link analysis, behavioural profiling, and AI-driven anomaly detection.
Q4. What data sources are used in crime pattern analysis?
Historical crime records, CDRs, CCTV, ANPR, OSINT, and financial intelligence.
Q5. How does Innefu support crime pattern analysis?
Through Prophecy Alethia, Intelelinx, Innsight, and AI Vision, offering predictive policing, CDR analysis, OSINT, and video analytics.




