The Rise of AI in Forensic Intelligence
Just a decade ago, digital forensics meant imaging drives, copying hard-disk bits and manually tracing deleted files. Fast forward, and investigators now confront petabytes of encrypted cloud files, mobile apps with disappearing data, IoT sensors streaming chaos, and they must act within hours, not months.
With the global digital forensics market set to grow from US $12.9 billion in 2025 to US $22.8 billion by 2030 (CAGR ~12 %) the pressure is plain: manual methods simply cannot keep pace.
That’s where artificial intelligence makes the leap. Automation, pattern-recognition, and intelligence fusion are transforming how evidence is discovered, correlated, and presented. AI isn’t doing away with the detective; it’s becoming their digital partner. From voice-to-text analysis of intercepted files to graph-based linking of devices, locations and identities, AI enables real-time triage of complex, multi-format evidence.
In this blog we’ll explore how AI is rewriting the rulebook of digital forensics, what’s changing, how investigations become faster and smarter, and why agencies that delay this shift risk falling behind. Because in the digital age, intelligence matters more than archives of data.
Key Takeaways
AI turns evidence overload into investigative intelligence: Machine learning automates repetitive forensic tasks and surfaces high-value clues instantly.
Forensic workflows are becoming proactive, not reactive: AI-enabled systems detect patterns and connections before manual review even begins.
Multimodal data fusion is the new gold standard: Combining text, image, voice, and video data creates deeper context for every case.
Explainable AI ensures legal defensibility: Transparent audit trails preserve the integrity and admissibility of digital evidence.
Innefu’s Argus bridges technology and trust: Purpose-built for national agencies, it enables real-time forensic analysis across devices, networks, and data sources, securely on-premise.
From Manual Analysis to Machine Intelligence
For decades, digital forensics relied on manual extraction, painstaking file-by-file review, and cross-checking data across isolated tools. Investigators often faced the frustrating reality that analyzing a single smartphone image or hard drive dump could take weeks, by which time the suspect may have changed networks, devices, or even identities.

Traditional Forensic Bottlenecks
The challenges of traditional forensics were as procedural as they were technical. Evidence acquisition was linear, case triage was manual, and every stage depended heavily on human bandwidth. Investigators had to sift through terabytes of logs, videos, and chat histories, often stored in fragmented silos.
Encrypted devices made extraction harder, while the growing number of communication platforms added another layer of complexity. With each new app, cloud container, or device type, a new tool or technique had to be learned. Human fatigue, cognitive overload, and the absence of integrated analysis meant that actionable intelligence was often delayed or missed altogether.
How AI Changes the Equation
Artificial Intelligence fundamentally reshapes this investigative model. What once took weeks can now be done in hours. Machine learning algorithms can automatically categorize files, filter duplicates, and identify hidden relationships between data fragments.
AI learns to recognize behavioral anomalies like unusual logins, communication bursts, or financial trails, across massive datasets within seconds.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) deciphers multilingual chat logs, voice notes, and even coded messages across regional dialects, providing investigators clarity where manual translation would fail. Meanwhile, AI-powered visual analytics can fuse information from CDRs, CCTV footage, and messaging data to highlight correlations that would be invisible to the human eye.
The result isn’t just faster processing, it’s smarter investigation. AI reduces manual workload while amplifying insight, ensuring that no critical clue is lost in the flood of digital noise.
AI-driven forensic automation platforms like Innefu’s Argus embody this transformation. By integrating device analysis, communication data, and OSINT feeds into a single forensic workflow, Argus helps investigators move from reactive analysis to proactive discovery, connecting clues across devices, channels, and timelines with precision and speed.
Core Applications of AI in Digital Forensics
Artificial Intelligence is redefining how investigators process, analyze, and correlate digital evidence. From classifying terabytes of data to identifying hidden links between suspects, AI-powered forensics ensures faster, more accurate, and context-aware results.
AI for Evidence Classification & Prioritization
Investigators often start with vast amounts of data: drives, mobile extractions, emails, or logs, with little idea where the crucial evidence lies. AI automates this first and most time-consuming step.

- Automated triage: AI scans and flags potentially relevant files, drastically reducing manual workload.
- Intelligent tagging: Deep learning models categorize files by type (images, text, videos, audio) and label them based on forensic relevance.
- Anomaly detection: Algorithms highlight irregularities: altered timestamps, duplicate entries, or encrypted data fragments.
- Visual object recognition: Object detection models identify weapons, faces, or vehicles in thousands of multimedia files.
Impact: What once took weeks of human review now takes hours, allowing investigators to act on insights faster.
NLP for Chat & Document Analysis
Unstructured text: from messages, social media, or reports, is one of the hardest data types to analyze manually. Natural Language Processing (NLP) brings structure and meaning to this chaos.

- Multilingual text decoding: NLP reads and interprets multilingual conversations, code words, and slang.
- Alias correlation: AI links user aliases, phone numbers, or email IDs across multiple communication platforms.
- Sentiment & intent detection: Detects aggression, threats, or collusion within chat exchanges.
- Keyword intelligence: Identifies recurring keywords and phrases associated with criminal activity or planning.
Impact: NLP transforms plain text into actionable intelligence, connecting words, context, and intent across data silos.
Image & Video Forensics
In visual evidence analysis, AI unlocks capabilities far beyond the human eye. From deepfake detection to movement tracking, image analytics enhances the accuracy and reliability of visual forensics.
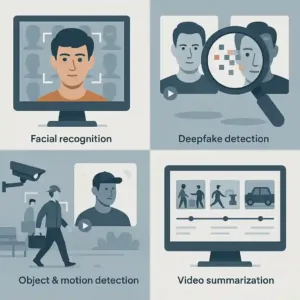
- Facial recognition: Matches suspects across images, CCTV footage, or social media.
- Deepfake detection: AI examines pixel-level inconsistencies to spot manipulated visuals.
- Object & motion detection: Identifies unusual activities, such as loitering or object exchange.
- Video summarization: Compresses long recordings into event-based summaries for quick review.
Products like AI Vision enable person re-identification, license plate tracking, and crowd behavior analysis, critical for law enforcement and security agencies.
Impact: AI makes video evidence analysis faster, more scalable, and contextually precise.
Predictive Link & Network Analysis
Criminal networks often hide behind fragmented digital trails. Graph-based AI analysis reveals these hidden relationships across devices, transactions, and communications.
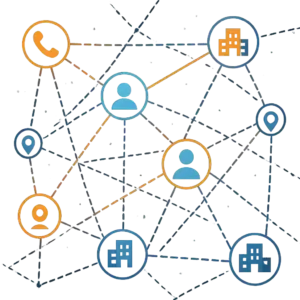
- Graph visualization: Connects entities such as phone numbers, accounts, and locations to reveal relationship maps.
- Pattern prediction: Identifies emerging criminal or financial patterns based on historical data.
- Cross-platform correlation: Links call data records (CDR), social media activity, and OSINT inputs.
- Anomaly mapping: Detects suspicious clusters or unusually connected nodes in the network.
Innefu’s Prophecy Suite uses fusion intelligence to correlate structured and unstructured data streams, enabling proactive threat mapping.
Impact: Investigators can uncover hidden networks and predict criminal movement before the next incident occurs.
Voice & Audio Forensics
Voice evidence provides critical leads, but manual analysis is often slow and error-prone. AI automates speech recognition and pattern matching for faster, more reliable results.

- Voiceprint identification: Matches a suspect’s voice against known samples using spectral features.
- Speaker separation: Distinguishes and labels individual speakers in multi-party recordings.
- Speech-to-text transcription: Converts large audio sets into searchable text for deeper analysis.
- Emotion detection: Identifies stress, urgency, or deceit in voice patterns.
Impact: AI voice forensics enables faster verification of threats and reconstruction of crucial conversations with near-human accuracy.
Behavioral Analytics & Timeline Reconstruction
Understanding the when, where, and how of suspect behavior is key to building a strong case. AI models piece together fragmented data to recreate detailed digital timelines.
- Activity sequencing: Maps device usage patterns, chat timestamps, and login histories.
- Location correlation: Cross-references GPS logs, CDR data, and CCTV feeds for movement verification.
- Behavioral profiling: Builds digital profiles based on browsing, messaging, and file access patterns.
- Incident simulation: AI reconstructs event flows, highlighting cause-effect sequences in criminal activities.
Impact: Investigators gain a 360° view of suspect behavior, transforming disconnected data into a coherent storyline of the incident.
The New Forensic Workflow: AI-Augmented Investigation
The fundamentals of digital forensics remain unchanged: identify, preserve, collect, analyze, correlate, and report.
What has evolved is how each of these stages is executed.
AI doesn’t replace investigators; it amplifies their capabilities: enabling faster, smarter, and more defensible investigations.
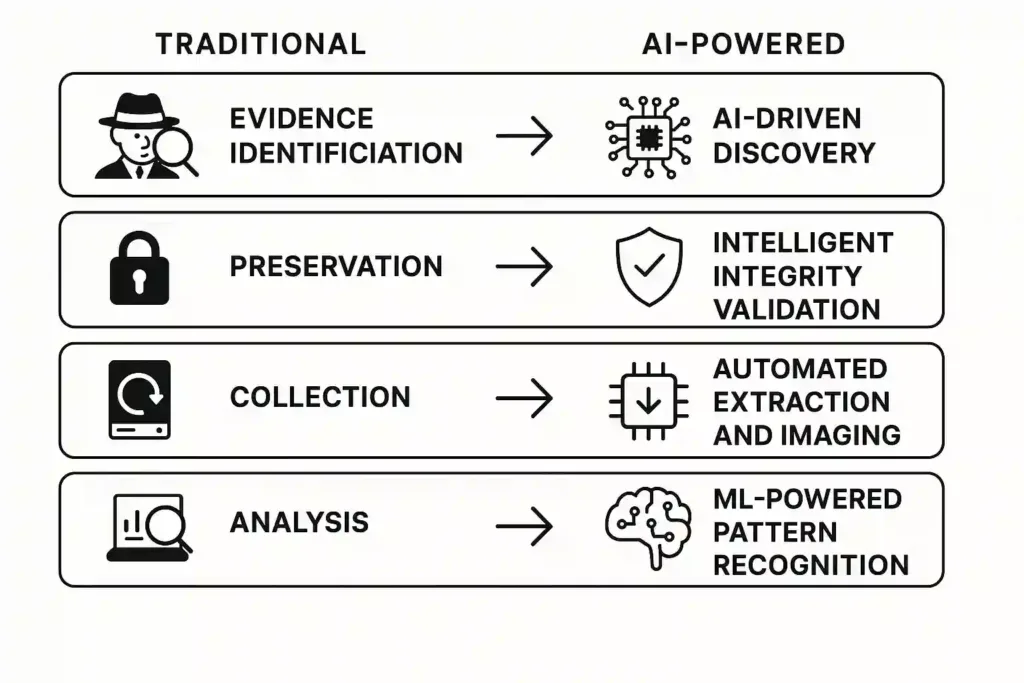
Traditional vs AI-Enhanced Forensic Workflow
Evidence Identification → AI-Driven Discovery
Traditional: Investigators manually scan through drives, devices, or cloud logs to determine relevant evidence sources.
AI-Enhanced: AI algorithms automatically detect and categorize digital artifacts, from devices and file types to specific log formats or communication channels.
Benefit: Rapid scoping of evidence sources, even across distributed environments. Outcome: Investigators save critical hours during early triage and can prioritize high-value data immediately.
Preservation → Intelligent Integrity Validation
Traditional: Manual hash generation ensures evidence hasn’t been tampered with, but human error can compromise accuracy.
AI-Enhanced: Automated integrity checks verify data authenticity in real time through hash validation and anomaly detection.
Benefit: Minimizes manual errors and ensures the forensic image remains court-admissible. Outcome: Evidence preservation becomes tamper-proof, consistent, and verifiable end-to-end.
Collection → Automated Extraction and Imaging
Traditional: Device imaging and metadata extraction are labor-intensive and time-consuming.
AI-Enhanced: Machine-driven acquisition tools perform automated disk imaging, metadata capture, and log parsing at scale.
Benefit: Enables simultaneous imaging of multiple devices without compromising the chain of custody. Outcome: The collection stage becomes scalable and traceable, ideal for large-scale investigations.
Analysis → ML-Powered Pattern Recognition
Traditional: Analysts manually sift through data, correlating logs, chats, and files.
AI-Enhanced: Machine learning models detect anomalies, recurring patterns, and outliers across structured and unstructured data.
Benefit: Speeds up evidence review and uncovers connections invisible to human analysis. Outcome: Investigations move from reactive discovery to proactive insight generation.
Correlation → Graph AI for Multi-Format Fusion
Traditional: Correlation across different data formats (CDR, CCTV, OSINT) often takes weeks.
AI-Enhanced: Graph-based AI links entities: calls, locations, accounts, and messages, into a single relational map.
Benefit: Provides investigators a unified, 360° view of networks and events. Outcome: Enables cross-domain intelligence, revealing links between physical and digital evidence.
Reporting → Auto-Generated Forensic Summaries
Traditional: Creating court-ready forensic reports requires manual documentation and validation.
AI-Enhanced: AI-generated reports include timelines, integrity logs, and evidence lineage automatically.
Benefit: Reduces human workload while maintaining evidentiary standards. Outcome: Reports are consistent, auditable, and ready for submission to judicial or enforcement authorities.
AI doesn’t change the chain of custody, it strengthens it. Every automated process leaves a verifiable audit trail, ensuring traceable evidence lineage from acquisition to courtroom presentation.
The Road Ahead: AI as the Investigator’s Force Multiplier
The future of digital forensics lies in multimodal intelligence: where text, video, audio, and sensor data converge to paint a complete picture of an incident. Investigators will no longer work in silos; instead, AI will fuse insights from multiple evidence types in real time, revealing narratives that once took weeks to uncover.
With edge-based forensics, AI models will soon operate directly in the field, analyzing data on secure devices, even in disconnected or high-risk environments. Meanwhile, generative AI will reconstruct crime scenes and visualize suspect movements, turning raw data into interactive, courtroom-ready evidence.

As cyber threats grow more complex, the next leap in forensics will be precision, not just speed; secure, explainable AI systems that investigators can trust.
Solutions like Innefu’s Argus are already redefining this transformation, enabling law enforcement and intelligence agencies to conduct faster, more accurate, and fully auditable investigations across digital domains.
The message is clear: AI isn’t replacing human expertise, it’s amplifying it. The investigator of the future won’t just analyze data; they’ll command an intelligent ecosystem built for national security.
FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions
- What is AI-driven digital forensics?
AI-driven digital forensics uses artificial intelligence and machine learning to automate evidence analysis, identify hidden patterns, and accelerate forensic investigations. - How does AI help in criminal investigations?
AI tools scan massive datasets, detect anomalies, and correlate data from chats, calls, videos, and networks — helping investigators uncover links and build strong cases faster. - What are examples of AI applications in digital forensics?
Examples include facial recognition, voice analysis, object detection in CCTV, NLP-based document review, and anomaly detection in communication logs. - Why is AI important for law enforcement forensics?
It enhances speed, accuracy, and scalability — enabling real-time insights from terabytes of data that would otherwise take weeks to analyze manually. - Can AI replace forensic investigators?
No. AI supports investigators by handling repetitive analysis and surfacing critical leads — the final judgment still rests with human experts. - What is multimodal forensic analysis?
It’s the integration of data from multiple formats — text, images, videos, and sensor feeds — into a unified AI-driven view for deeper investigation insights. - How does Innefu’s Argus enhance digital forensics?
Argus automates device imaging, metadata extraction, correlation, and reporting — creating an end-to-end forensic intelligence environment for government agencies. - How does AI ensure evidence admissibility in court?
By maintaining audit trails, cryptographic hashes, and chain-of-custody logs that validate the authenticity and integrity of all digital evidence. - What are the challenges of AI in digital forensics?
Key challenges include encrypted data, bias in algorithms, and the need for explainability to meet legal and ethical standards. - What’s the future of AI in digital forensics?
Expect a shift toward edge forensics, generative AI for scenario reconstruction, and real-time analysis across text, voice, and video data streams.




